Overview of Electric Vehicle Chargers
The surge in electric vehicle (EV) popularity has been astounding. As of 2023, millions of EVs cruise our roads, representing a significant leap towards sustainable transportation. A crucial component of this ecosystem is the Electric Vehicle chargers. Understanding the variety of EV chargers available is essential for potential EV owners, infrastructure planners, and enthusiasts alike. This article delves deep into the types of EV chargers, their unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
1. Introduction to EV Charging

2. Level 1 Chargers
Power Range: Up to 2 kW
Overview: Level 1 chargers utilise a standard 120V AC outlet, which is typically available in most households. It’s the most basic form of EV charging and often serves as the starting point for new EV owners.
Advantages:
- Universal Availability: Almost every home or establishment with electricity has access to Level 1 charging.
- Cost-effective: There’s no need for additional equipment or infrastructure.
Disadvantages:
- Slower Charging Times: It can take upwards of 20 hours to fully charge a depleted battery, making it unsuitable for vehicles with large battery capacities or for those in a hurry.

3. Level 2 Chargers
Power Range: 3.3 kW to 19.2 kW
Overview: The next step up, Level 2 chargers, require a 240V circuit. This is the same kind of power source used by many household appliances, like dryers.
Advantages:
- Versatility: Applicable for home, workplace, and public charging.
- Faster Charging: Typically fills up an EV battery in 4-8 hours, making overnight charging or workplace charging feasible.
Disadvantages:
- Installation Costs: While not exorbitant, setting up a Level 2 charger at home can incur costs, especially if electrical upgrades are needed.

4. Level 3 Chargers (DC Fast Charging)
Power Range: 20 kW to 350 kW+
Overview: These are the high-powered chargers, often seen at commercial establishments or along highways.
Advantages:
- Rapid Charging: Can charge most EVs up to 80% in under an hour, making long road trips feasible.
- Commercial Viability: Due to their speed, these are attractive options for businesses looking to offer charging as a service.
Disadvantages:
- Costly Infrastructure: They require significant electrical infrastructure, making them expensive to install.
- Battery Health Concerns: Continual use of fast chargers can reduce the longevity of EV batteries due to heat generation.
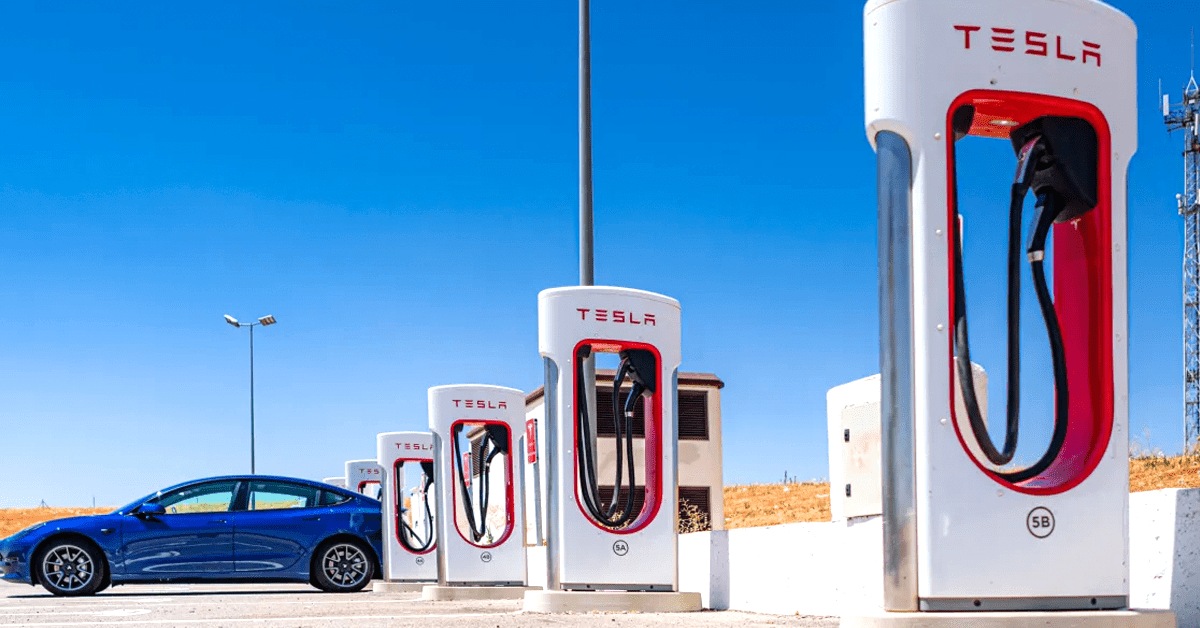

5. Tesla Superchargers
Tesla, the EV giant, has its proprietary network of high-speed chargers known as Superchargers. Pushing out up to 250 kW, they are strategically located to facilitate long-distance travel for Tesla owners.
Advantages:
- Exclusivity: Ensures that Tesla drivers have a consistent charging experience.
- Speed: Among the fastest charging solutions available.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Compatibility: Only usable by Tesla vehicles, excluding other EV owners.
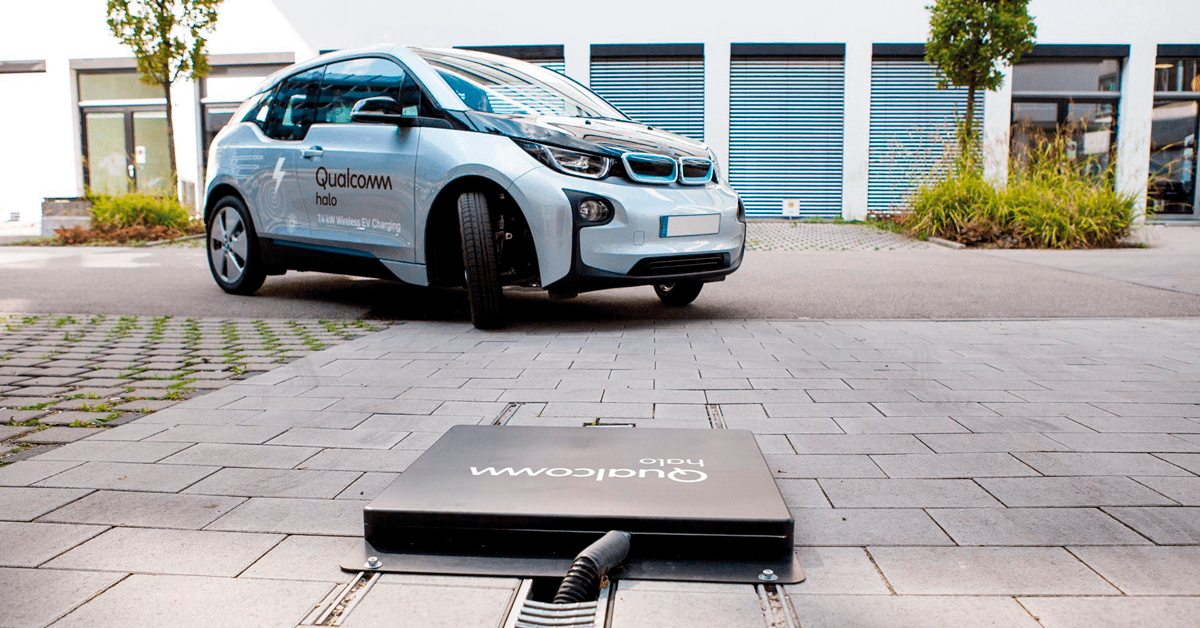
6. Wireless Charging
Wireless EV charging is still in its nascent stages but promises a future of drive-up-and-charge convenience.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Eliminates the need for physical cables.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: No physical connection means less damage over time.
Disadvantages:
- Efficiency: Current wireless solutions are less efficient than traditional methods, leading to longer charge times.
- Cost: Premium pricing for the convenience and technology.
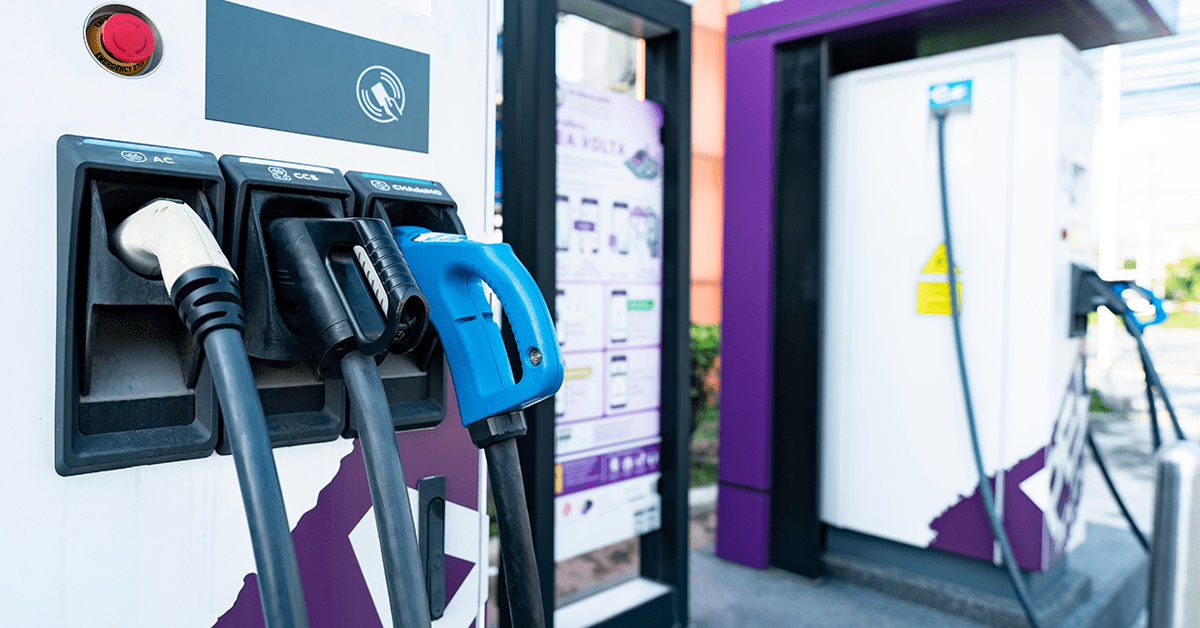
7. Public vs. Private Charging Stations
Private Charging: Typically refers to home-based charging solutions, where the EV owner has control over the charger’s access.
Public Charging: Available to the general public, often found in malls, parking lots, and other public spaces.

8. The Future of EV Charging
As the EV market matures, so will the charging infrastructure.
- Ultra-fast Chargers: Research is pushing the boundaries of charging speeds, with 350 kW chargers already in the horizon.
- Universal Charging Standards: Efforts are being made to standardize charging connectors to ensure compatibility across all EV brands.
- Green Charging: As the grid becomes greener, EVs will transition from being low-emission vehicles to zero-emission vehicles when charged.
9. Conclusion
#EV Chargers
#Green Charging
#Future of Transportation
About WDD Malaysia
In the competitive field of website design, WDD Malaysia excels as a website designer dedicated to enhancing business performance through innovative branding and tailored digital services. They serve key sectors such as manufacturing, oil & gas, engineering and logistics, creating custom, appealing websites that are optimised for conversions and user engagement. Their approach includes a strong emphasis on mobile-first design, advanced SEO, and ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal performance. WDD Malaysia’s branding services extend to creating visual identities and integrating digital marketing strategies, making them a go-to for businesses facing issues like inadequate lead generation and poor online visibility.